08.24.18
The addition of anti-skinning agents to paint prevents the formation of skin, which is formed due to oxidation and polymerization of the binder at the paint-air interface. The anti-skinning agents inhibit or delay the oxidative processes, which lead to skin formation during both storage and application. They do not affect the color and film formation tendencies. The formation of skin is directly proportional to the temperature of the environment the paint is exposed to, and the solid content in the paint. Poor formulation, production faults and faults in processing also contribute to this problem. Also, the skin formed blocks the nozzles of the spray painting equipment and impair the appearance of the coat. The loss occurred due to skinning is estimated at three to five percent.
Prevention Measures include proper sealing of paint pails, anti-skinning agents, straining paint through a nylon strainer, storage of paint in cool areas and replacing air by nitrogen in headspace of storage containers. The only disadvantage of using anti-skinning agents is the increase in drying time due to anti-oxidant property. Dosage should be carefully optimized to attain right level of anti-skinning activity and drying time.
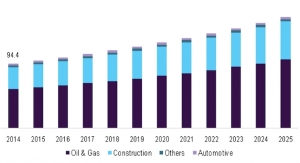
Anti-skinning agents are generally used as a solvent-borne coating, mainly in alkyd-based paints. The increasing use of methylethylketoxime (MEKO) skinning agent in alkyd based paints used for printing inks, industrial wood, pigment dispersions, and general industrial end-uses to prevent skinning factor are fueling the growth of global anti-skinning agents market. Moreover, oximes and phenols are well-known as oxygen scavengers and largely helps in reducing oxidation rates. Hence, they are the primary constituent in most anti-skinning agents. MEKO is the most widely used anti-skinning agent and is added in very small proportions to the paint (0.5 percent). Retention aids prevent applied paint films from drying too quickly. Furthermore, solvents used as anti-skinning agents dissolve the components which form skins.
The growing demand for anti-skinning agents from printing inks industry is the major driver for the growth of anti-skinning market globally. The decorative end-use segment is the fastest growing segment in the anti-skinning agent market. The factors such as the growing GDP and rapid urbanization in Asia Pacific, primarily in China, and India creates a highly conducive environment for market growth. Due to which, the demand for new and improved infrastructure is increasing, enabling the growth of decorative paints, which in turn is fueling the anti-skinning agents market during the forecast period.
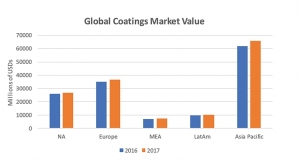
Asia Pacific market is expected to grow at a rapid pace due to demand from the expansive construction industry, which in turn driving paints and anti-skinning agents market. The growing urbanization, rising paints and coatings industry, and the rise in disposable incomes of the population are the major drivers for the burgeoning growth of anti-skinning agents in the Asia Pacific region. For instance, according to the India Paint Association, the paint industry in India is valued at US$ 7.6 billion in 2017 and is expected to grow to US$ 10.8 billion by 2020. Also, as per statistics released by India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF)—a Trust established by the Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India—the Indian government plans to invest US$ 376.53 billion in infrastructure development over the following three years.
Growth in the developed world i.e. North America and Europe is dependent on the market of the construction industry. These markets are matured and growth is typically slower than in emerging markets. With increased environmental regulations in these countries, new technologies and products are been developing at a rapid pace. Hence, allowing the anti-skinning agent market to grow at a descent rate.
Latin America is experiencing mixed growth figures. Brazil is the largest market of anti-skinning agents in Latin America. However, Brazil has experienced a slight slowdown in the construction industry, but the countries such as Colombia, Mexico, and Argentina have experienced moderate to rapid growth in construction activities, which in turn allowing the significant growth of anti-skinning agents market over the following years.
For more, click here.

Prevention Measures include proper sealing of paint pails, anti-skinning agents, straining paint through a nylon strainer, storage of paint in cool areas and replacing air by nitrogen in headspace of storage containers. The only disadvantage of using anti-skinning agents is the increase in drying time due to anti-oxidant property. Dosage should be carefully optimized to attain right level of anti-skinning activity and drying time.
Anti-skinning agents are generally used as a solvent-borne coating, mainly in alkyd-based paints. The increasing use of methylethylketoxime (MEKO) skinning agent in alkyd based paints used for printing inks, industrial wood, pigment dispersions, and general industrial end-uses to prevent skinning factor are fueling the growth of global anti-skinning agents market. Moreover, oximes and phenols are well-known as oxygen scavengers and largely helps in reducing oxidation rates. Hence, they are the primary constituent in most anti-skinning agents. MEKO is the most widely used anti-skinning agent and is added in very small proportions to the paint (0.5 percent). Retention aids prevent applied paint films from drying too quickly. Furthermore, solvents used as anti-skinning agents dissolve the components which form skins.
The growing demand for anti-skinning agents from printing inks industry is the major driver for the growth of anti-skinning market globally. The decorative end-use segment is the fastest growing segment in the anti-skinning agent market. The factors such as the growing GDP and rapid urbanization in Asia Pacific, primarily in China, and India creates a highly conducive environment for market growth. Due to which, the demand for new and improved infrastructure is increasing, enabling the growth of decorative paints, which in turn is fueling the anti-skinning agents market during the forecast period.
Asia Pacific market is expected to grow at a rapid pace due to demand from the expansive construction industry, which in turn driving paints and anti-skinning agents market. The growing urbanization, rising paints and coatings industry, and the rise in disposable incomes of the population are the major drivers for the burgeoning growth of anti-skinning agents in the Asia Pacific region. For instance, according to the India Paint Association, the paint industry in India is valued at US$ 7.6 billion in 2017 and is expected to grow to US$ 10.8 billion by 2020. Also, as per statistics released by India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF)—a Trust established by the Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India—the Indian government plans to invest US$ 376.53 billion in infrastructure development over the following three years.
Growth in the developed world i.e. North America and Europe is dependent on the market of the construction industry. These markets are matured and growth is typically slower than in emerging markets. With increased environmental regulations in these countries, new technologies and products are been developing at a rapid pace. Hence, allowing the anti-skinning agent market to grow at a descent rate.
Latin America is experiencing mixed growth figures. Brazil is the largest market of anti-skinning agents in Latin America. However, Brazil has experienced a slight slowdown in the construction industry, but the countries such as Colombia, Mexico, and Argentina have experienced moderate to rapid growth in construction activities, which in turn allowing the significant growth of anti-skinning agents market over the following years.
For more, click here.